Ductile iron, also called spheroidal or nodular iron, is a type of cast iron known for its high strength and durability. It has graphite substantially spheroidal in shape that gives excellent machinability.
This material is often used in the construction of pipes and fittings and in automotive and industrial applications. While ductile iron has many advantages, certain specifications must be met to ensure that its expected performance is met.
ASTM International sets the international standard for specification for ductile iron. These specifications are usually indicated in the contract or purchase order document from foundries.
Grade 60-40-18
Grade 60-40-18 ductile iron is a type of cast iron known for its excellent strength and ductility. It is a ferrous alloy composed primarily of iron, carbon, and silicon. It is primarily used in applications where strength and ductility are paramount, such as valves, pumps, and other pressure-containing equipment. The grade’s high carbon content provides excellent tensile strength, allowing for components to hold up under pressure tightness.
Additionally, its high ductility allows components to bend and flex without breaking, making it ideal for applications requiring components to withstand shock, vibration, and other dynamic forces.
Grade 60-40-18 ductile iron comprises 60% iron, 40% carbon, and 18% silicon, with other trace elements such as manganese, sulfur, and phosphorus. It has a tensile strength of 60 ksi and a yield strength of 40 ksi. It has an elongation of 18%, which gives it its ductility, allowing it to bend or deform without breaking or cracking.
When used in castings, it can be machined using traditional methods, such as drilling, tapping, and milling. It can also be welded and brazed, although an appropriate heat treatment may be required to achieve the desired strength and ductility.
Grade 65-45-12
Grade 65-45-12 ductile iron is a particular type of iron with a higher tensile strength than other forms of iron. This type of iron is often used in applications that require a higher strength-to-weight ratio and increased shock resistance.
This iron alloy is composed of 65% iron, 45% carbon, and 12% manganese. This combination of elements gives the iron alloy good ductility and impact strength, which means it can be formed into complex shapes and withstand impacts better. It is more corrosion-resistant than regular iron and can be used in applications requiring increased wear resistance.
It has a high tensile strength of up to 65,000 psi. This makes it suitable for various applications, such as bearing housings, gears, and other components that require high strength and durability.
This ductile iron has excellent wear resistance, making it an ideal choice for components that need to withstand long-term use. It also has a high melting point of 1,475 degrees Celsius.
Grade 80-55-06
Grade 80-55-06 ductile iron is made by adding magnesium to regular cast iron. This increases the strength of the iron and makes it more corrosion-resistant. Its magnesium content produces a carbon-rich material that is then cooled and treated with heat, resulting in cast iron that has a high strength-to-weight ratio.
It is often used in applications where strength and durability are paramount. It is also preferred when a component must resist high-pressure levels, such as valves and pumps.
This type of ductile iron is a high-strength, ductile iron with a tensile strength of 80 ksi, yield strength of 55 ksi, and 6% elongation. The chemical composition of Grade 80-55-06 ductile iron consists of 3.90-4.20% carbon, 1.60-2.00% silicon, 0.45-0.75% manganese, and 0.30-0.80% phosphorus.
Grade 100-70-03
Grade 100-70-03 ductile iron is a high-grade material capable of withstanding loads up to 100,000 pounds per square inch (psi). It is also highly corrosion-resistant, making it an excellent choice for chemical and marine environments.
Isothermal heat treatment is required for this grade to have better properties. Its excellent machinability makes it a great choice for applications requiring precise tolerances.
How Grades of Ductile Iron Castings Are Determined

The most common test used to determine ductile iron grade is the Charpy Impact Test. This test measures the amount of energy required to break a test specimen cast material. The test results are then compared to a chart of international standards, which indicates the grade of the ductile iron. The higher the grade, the better the ductile iron’s strength and durability.
In addition to the Charpy Impact Test, other tests are used to determine the grade of ductile iron. The Rockwell Hardness Test is used to measure the hardness of the casting, while the Brinell Hardness Test is used to measure the ductile iron’s resistance to wear and tear.
The metallurgical analysis test determines the composition of the produced ductile iron. This test measures the amount of elements present in the material, such as carbon, silicon, and manganese.
Standard Specification of ASTM A536
ASTM 536 specification covers castings that are made from different cast iron grades. The first number in the grade designation refers to the tensile strength of the material, while the second and third numbers refer to the yield strength and percentage of elongation, respectively.
The first number in the grade designation refers to the tensile strength of the material, while the second and third numbers refer to the yield strength and percentage of elongation, respectively.
Mechanical Properties
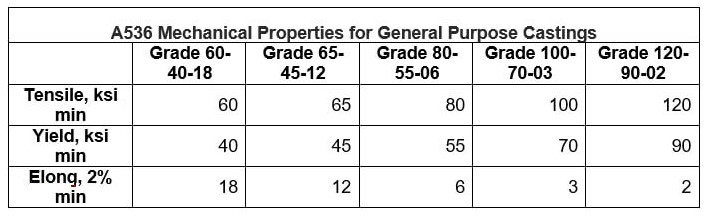
ASTM A536 is known for its exceptional mechanical properties. It has a tensile strength range of 60-85 ksi and a yield strength range of 35-50 ksi. ASTM A536 also has good impact resistance, with a minimum of 15 ft-lbs at room temperature. Additionally, it has excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for use in various industrial applications.
Chemical Composition

ASTM A536 mainly comprises iron, carbon, silicon, manganese, and phosphorus. The exact proportions of these elements vary depending on the grade, but the considered standard for chemical composition is at least 2.5% carbon, 1.25-2.5% silicon, and 0.5-1.5% manganese.
Heat Treatment
The ASTM A536 specifies the required temperature for heat treatment and the minimum cooling rate. It also outlines the methods for controlling the heat treatment process and the post-heat treatment inspection and testing requirements.
What Should Be Stated in a Ductile Iron Specifications Document

The ASTM 536 document should include information related to chemical compositions, physical properties, and mechanical properties.
Chemical composition should include various elements specified in the document and their required concentrations.
Heat treatment outlines the requirements for heat treatment of the ductile iron castings, including selecting suitable alloying elements and determining the heat treatment process parameters.
For mechanical properties, the document should include information related to the material’s tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation.
Physical properties, such as density, thermal expansion, and thermal conductivity, should be stated in the document. The document should also state other special requests, such as magnetic particle inspection dimensions, radiographic soundness, and surface finish.


