Stainless steel castings are used in many industries because of their mechanical properties. It is a versatile material that can be used in a variety of applications, from automotive parts to medical equipment. Despite its many advantages, some people may not know that stainless steel can also be cast.
This process is used to create various shapes and sizes for use in different applications. Casting stainless steel is a relatively simple process that can be done in-house or outsourced to a foundry.
It can be used in producing complex shapes and components. It is different from other metals that need other manufacturing processes.
Defining Stainless Steel Castings
Stainless steel casting is a specialized form of metal casting in which stainless steel is used as the main casting material.
Depending on the complexity of the part being created, the metal may need to be machined or otherwise worked with high temperatures to achieve the desired shape and size.
The parts produced from the process are often less expensive than those produced by welding or machining. The process also offers greater strength and corrosion resistance than other metal-forming processes.
The process is widely used in many industries, including medical, automotive, and industrial applications.
Stainless Steel Casting: How Do They Do It?
Metal outcomes with specific requirements require the use of stainless steel casting process.
Many industries use stainless steel. It includes construction industries, surgical tools, and many more.
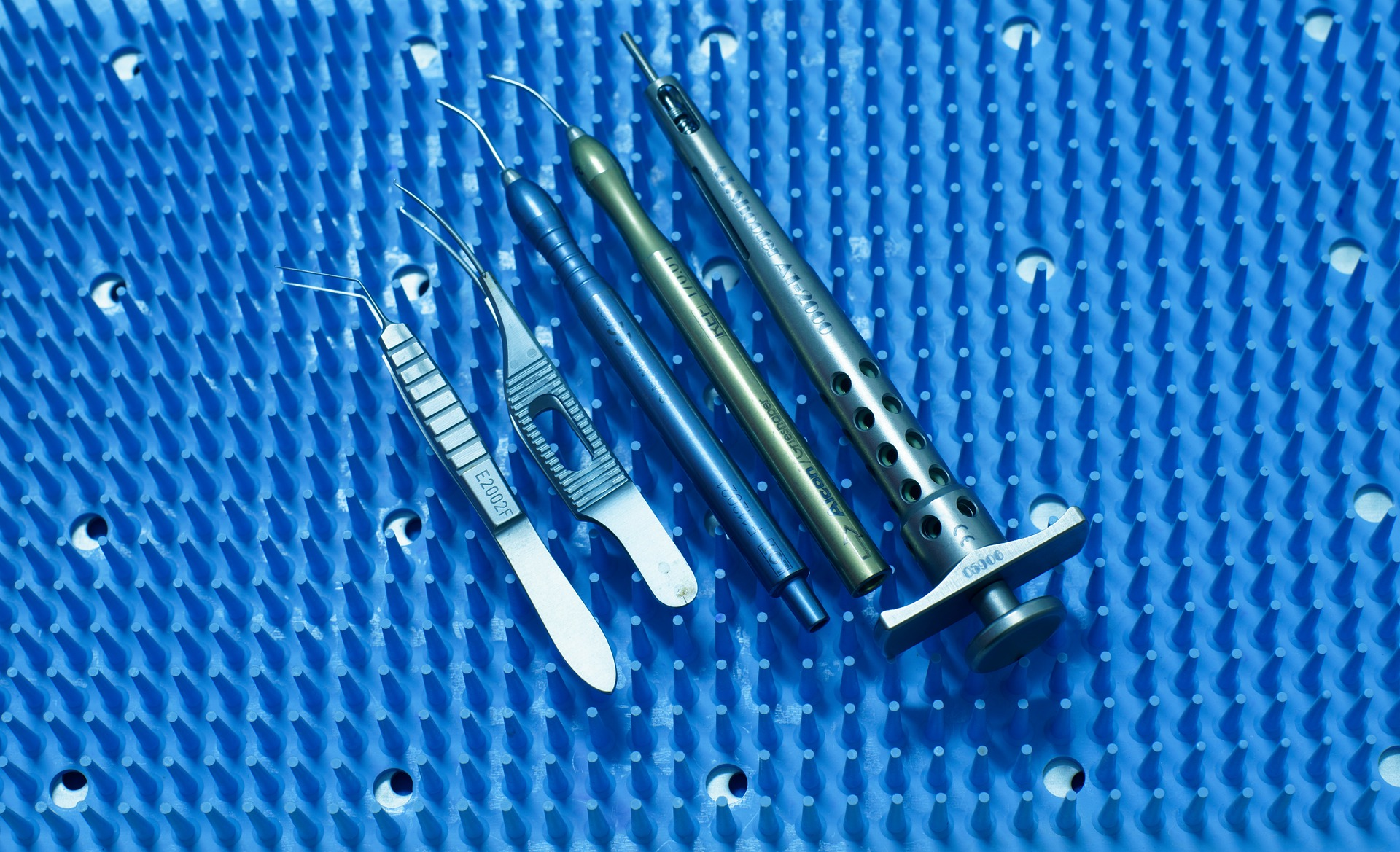

Preparation
Different alloys have different properties, such as melting points, strength, and corrosion resistance. Once the metal alloy is selected, it is melted down in either an electric arc furnace or a crucible furnace.
Different grades of steel have different characteristics, and it’s important to choose the grade that best suits the purpose of the casting. Once the grade is chosen, the next step is to prepare the steel for casting.
This involves heating the steel to a high temperature and allowing it to cool slowly in a controlled atmosphere.
Pouring of Molten Metal for Casting Stainless Steel
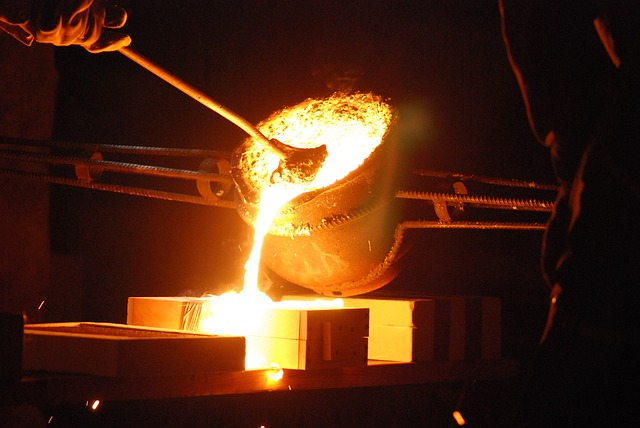

The molten stainless steel is poured into a metal mold that is designed to match the desired shape of the final product.
Pouring the molten metal into the mold is an integral part of the process. The metal must be applied at a specific temperature to ensure the proper adhesion and cooling of the metal.
The process of pouring molten stainless steel is a precise and intricate process that requires experienced professionals to ensure a successful outcome.
Cooling the Stainless Steel
The stainless steel will become solid and contract as soon as it cools. The contraction of the metal causes the surfaces to shrink, and this creates a thin layer of solidified metal.
This layer must be thick enough to support the weight of the casting. As the molten metal cools, it becomes more brittle and is more susceptible to cracking. If the metal is cooled too quickly, it can cause cracks and other imperfections in the casting.
The metal continues to contract, and the thin layer of solidified metal that was formed earlier begins to thicken. This causes the metal to become more rigid, and the thin layer of solidified metal is replaced by a thicker layer. The thicker layer of metal is stronger and more resistant to cracking.
The slow cooling process allows the stainless steels to regain some of its strength and malleability. The metal is then ready to be machined into its desired shape. The entire cooling process must be carefully monitored and controlled to ensure the best outcome for the casting.
Stainless Steel Investment Castings: What are They?
The stainless steel investment castings are particularly valued for their ability to produce high-precision parts that require tight tolerances and intricate details.

It is a cost-effective alternative to traditional metal manufacturing techniques such as machining and forging. The investment casting process offers a number of benefits, including superior strength, corrosion resistance, and a high level of repeatability.
The process of stainless steel investment casting begins by creating a wax pattern of the part to be cast. Wax patterns are coated with a ceramic slurry and allowed to harden. It then produces a shell mold casting. It leaves a hollow ceramic mold that is filled with molten metal.
The molten stainless steel is then allowed to cool and solidify. The ceramic shell provides a smooth surface finish.
It is able to produce parts with complex geometries and intricate details that are not possible with other methods.
Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steel Castings
Stainless steel casting has become a popular choice for many industrial applications due to its unique advantages over other metals.
This makes it ideal for stainless steel parts that need to withstand harsh environments and high temperatures.
It Possesses High Strength
One of its advantages is its strength. It’s a very strong material and can withstand high temperatures without weakening. This makes it ideal for parts that need to be exposed to extreme temperatures, such as those in engines, turbines, and other machinery.
With sand casting, it still possesses the same strength as other processes. However, the sand casting process can make it prone to stress corrosion cracking.
Superior Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel alloys have a protective layer over the steel, which makes it corrosion resistant. Its chemical composition also makes stainless steel resistant to most acids, alkalis, and other corrosive materials. The chromium content provides a natural barrier to oxidation.
This oxide film is extremely thin and can be easily damaged, so it’s important to maintain the integrity of the casting’s surface. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to ensure the corrosion resistance and its resistance to chloride solutions of the stainless steel casting.
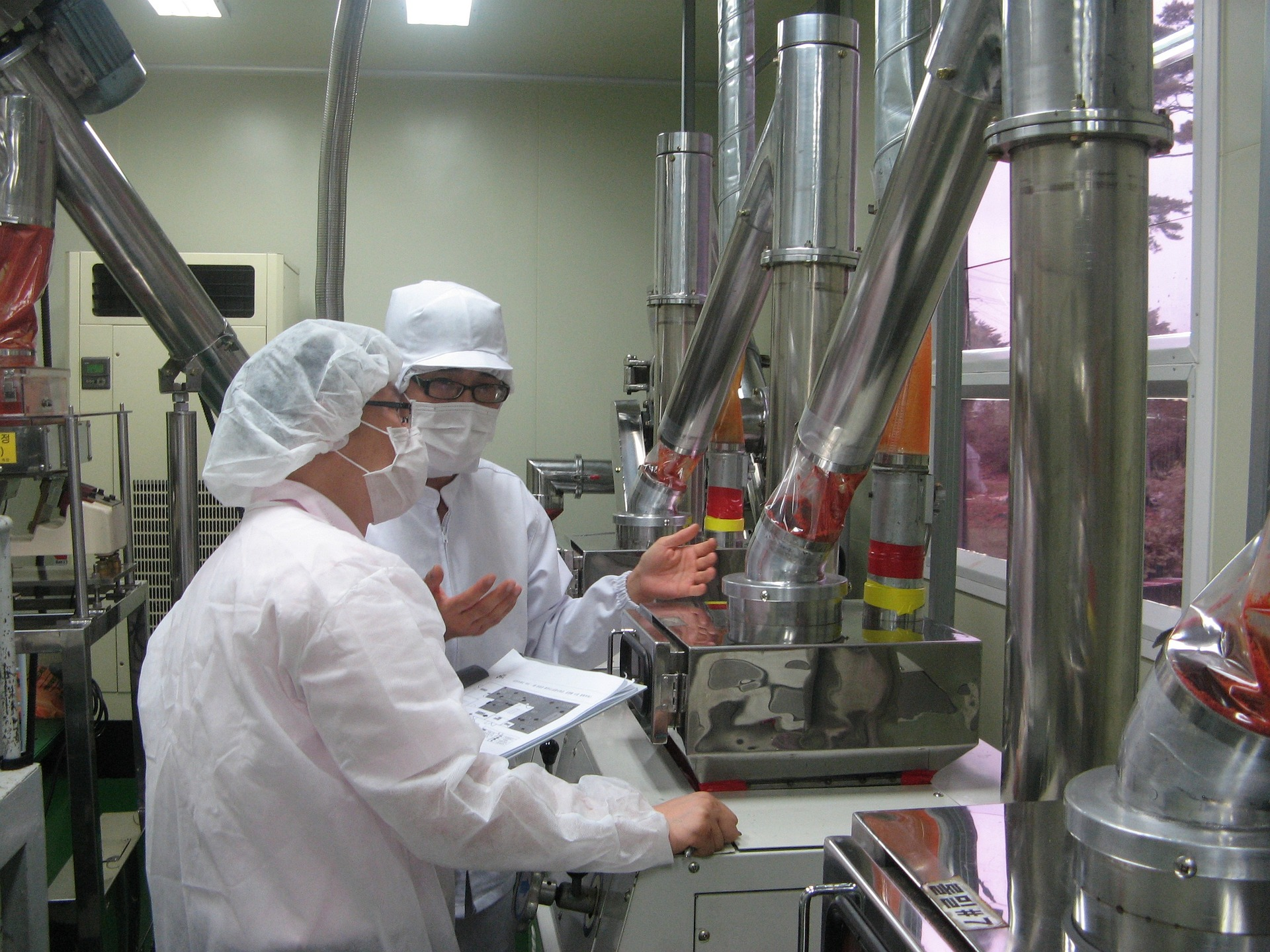

Food processing equipment is made of stainless steel materials. In each of these industries, corrosion resistance is often the key factor for choosing a material for a specific application.
Extreme Durability
The durability of stainless steel castings is due to their high chromium content. Stainless steel parts are an excellent choice for outdoor applications. It is also very resistant to high heat and intense pressure, which makes it perfect for applications in industrial settings.
The durability of stainless steel casting is further enhanced by its thermal stability. This makes it ideal for industrial applications, such as creating parts for engines, turbines, and other transmission components.
It remains in perfect condition even in extreme conditions and atmospheric conditions.
This makes it a cost-effective choice for projects that require long-term performance.
Aesthetically Pleasing
In addition to its mechanical properties, stainless steel casting is also aesthetically pleasing. It can be polished to a mirror-like finish, allowing it to be used for decorative purposes because of its chromium content. This makes it a popular choice for creating sculptures, jewelry, and other decorative items.
Its high-gloss finish and smooth surface make it a great option for parts and components that require a sleek, professional look. It is available in a variety of colors, allowing for parts and components to be tailored to a specific project or design.
Challenges of Casting Stainless Steel
Stainless steel casting is a popular process to cast stainless steel parts with complex geometries. However, it is not without its drawbacks.
High-Cost
Stainless steel casting is expensive. It requires a high level of precision and skill to properly cast stainless steel parts. It also requires a lot of time, effort, and resources. As a result, stainless steel castings tend to be much more expensive than parts created using other methods.
Generally, stainless steel castings are one of the more expensive processes due to the difficulty of working with metal.
This process involves the use of several wax patterns, which are then filled with a ceramic slurry and undergoes heat treatment until the wax pattern melts away.
The entire process is time-consuming and labor-intensive, which can add to the cost.
Very Hard
One of the main drawbacks of casting stainless steel is its hardness. While this is beneficial for some applications, it can be a disadvantage for others.
The hardness of stainless steel casting is determined by the amount of carbon present in the alloy. The more carbon present, the harder the stainless steel casting will be. The hardness is beneficial in certain applications, such as those requiring wear and tear resistance. But steel with a low carbon content is recommended for steel castings that require machining or forming the part.
The cracking or fracturing during the casting process can lead to further delays in production and additional costs for repairs or replacements.
Prone to Porosity
Porosity can cause a number of problems in stainless steel casting. It can weaken the casting and reduce its strength and durability. It can also cause the casting to fail inspections, resulting in costly delays in production.
Therefore, it is important to take steps to reduce porosity in stainless steel casting. This includes using the correct alloying ingredients, thoroughly cleaning the mold, monitoring the casting temperature, and using proper pouring techniques.
Uses of Stainless Steel Castings
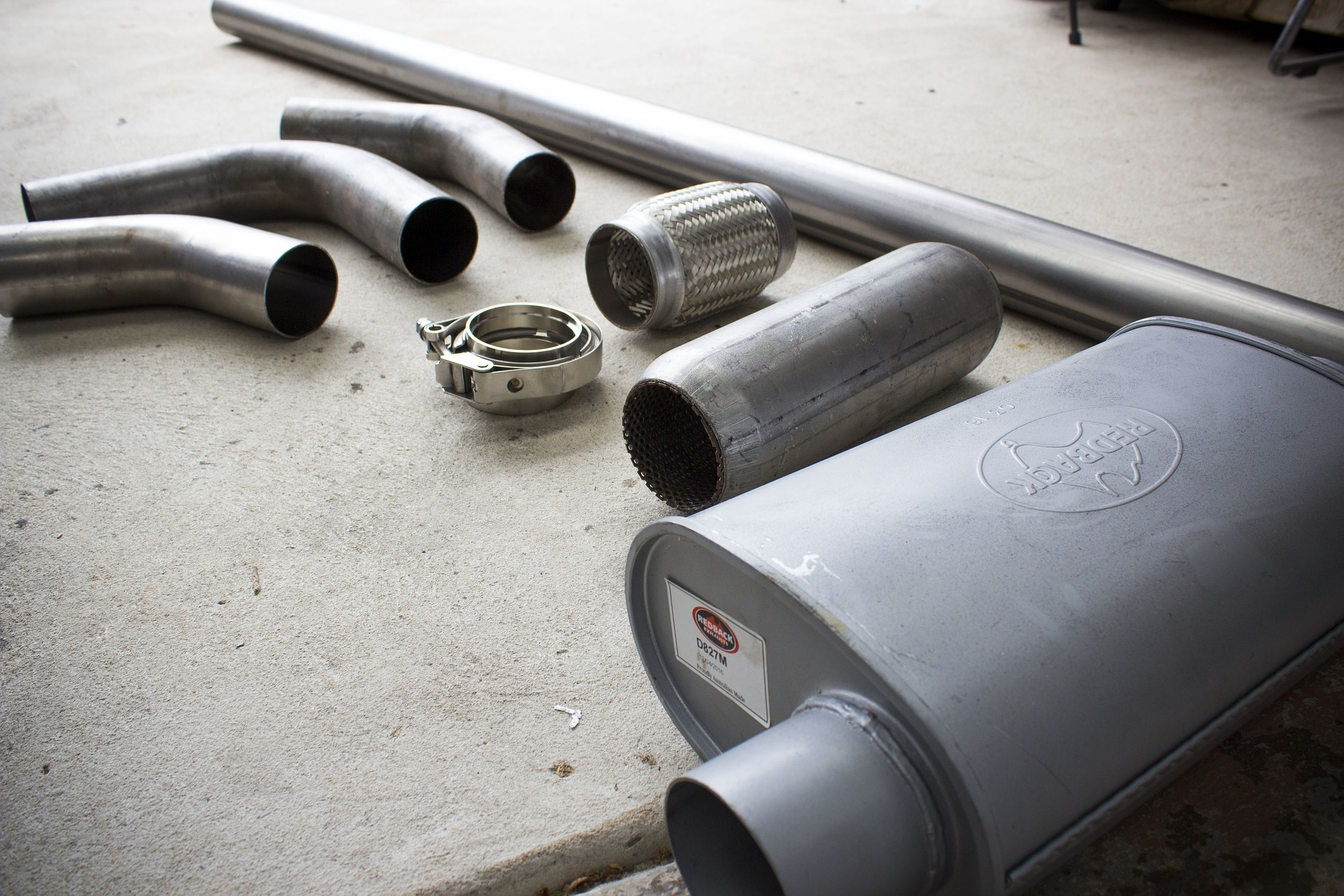

Stainless steel castings are well known for their strength and resistance to corrosion and rust. This makes them ideal for use in the most demanding of environments. One of the most common uses of stainless steel castings is in the automotive industry. They are used in the manufacture of engine components and in the construction of exhaust systems.
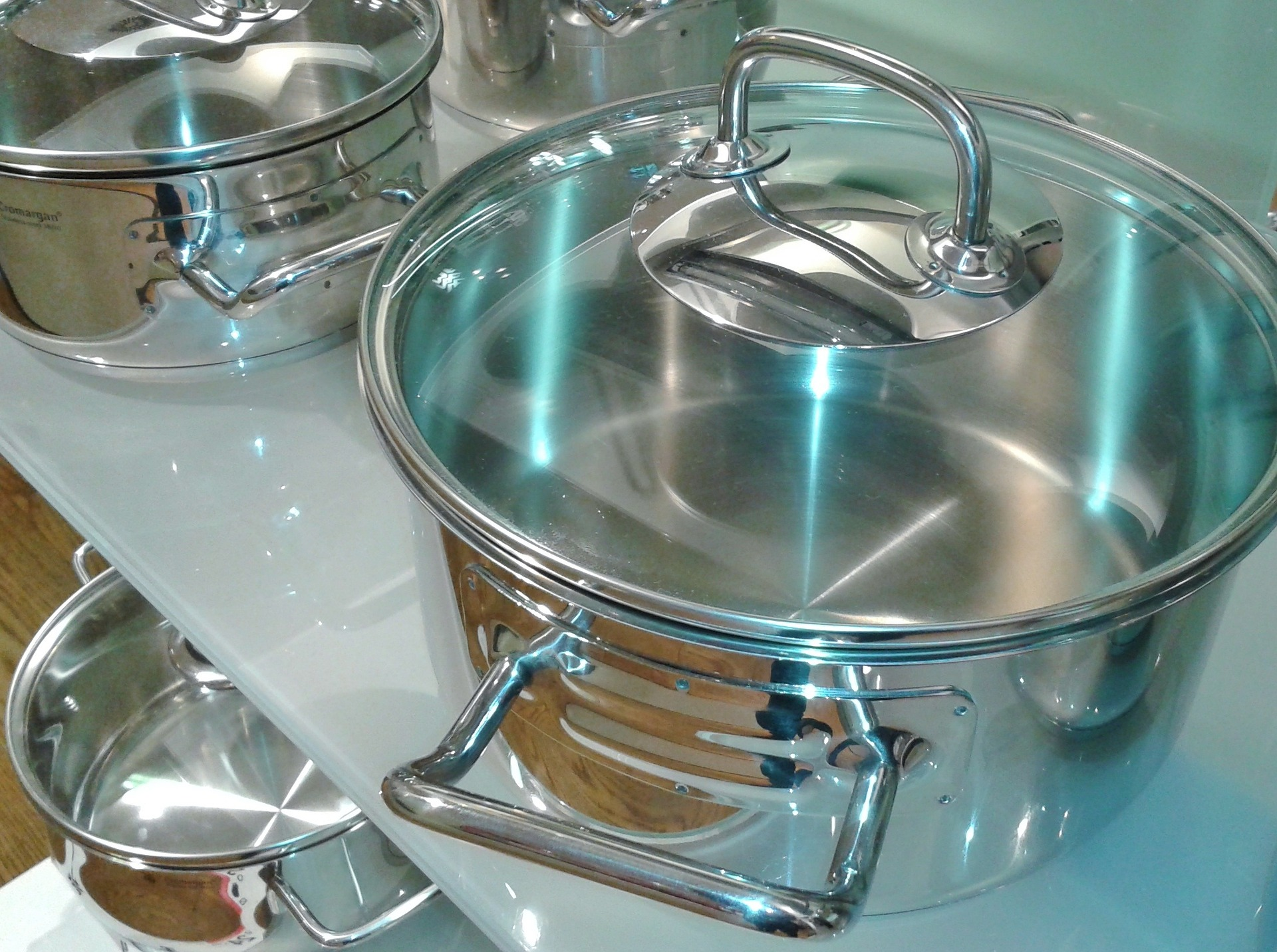

Stainless steel castings are also widely used in the food processing industry. Their non-toxic and corrosion-resistant properties make them perfect for use on food contact surfaces, such as cookware and food processing equipment. This makes them ideal for use in the food industry, where contamination and safety are of paramount importance.
Stainless steel castings are also used in the construction of medical equipment, such as surgical instruments and implants. Their strength and resistance to corrosion and rust make them an ideal choice for a variety of uses.