This manufacturing process involves injecting molten aluminum using die-casting equipment into a reusable steel mold or die. The result is a cost-effective, high-quality part with excellent mechanical properties and surface finish. This process is best for casting an aluminum alloy.
Aluminum Die Casting Process
Aluminum castings are predominant in aerospace industry and other high-temperature environments. Its strength-to-weight ratio and high performance properties are critical factors in these industries. Because of its aluminum oxide layer, it produces an aluminum casting with excellent corrosion resistance.
Because of its high thermal conductivity, it is also useful in consumer products like electronics as heat sinks and other components.
Creating Die Cast Mold for Aluminum Castings
Creating die-casting dies or die-casting tooling is designed using computer-aided design (CAD) software, allowing the designer to create a detailed cast aluminum model. The die-cast design considers part geometry, draft angles, and parting lines.
The die is machined from a steel block using CNC machines. The machining process involves cutting and shaping the steel to create the cavities and cores to form the custom aluminum parts.
The die is then heat-treated to harden the steel and improve its durability. After heat treatment, the die is finished to ensure the desired final product’s correct dimensions and surface finish.
Melting The Aluminum: Preparation and Pouring
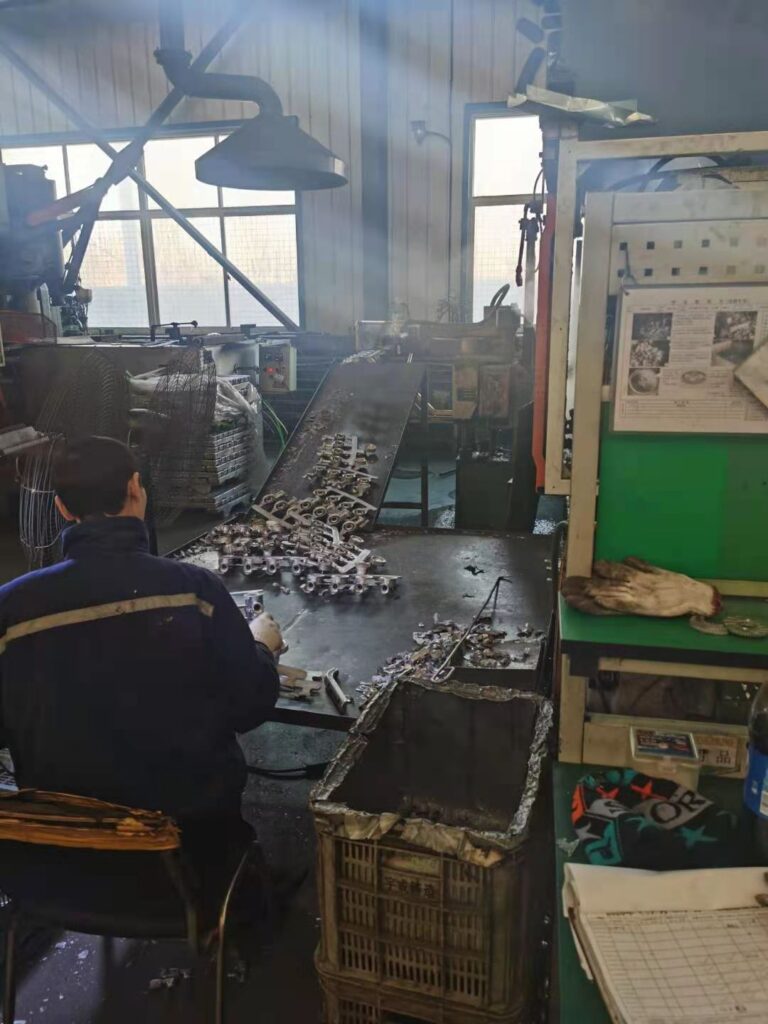

The preparation and pouring of molten metal are critical steps in the aluminum die-casting process, as the quality and consistency of the aluminum casting depend on the quality and precision of the pouring process.
Once the pure aluminum has melted, casting alloys can be added to the molten metal to modify its properties. Alloying elements can include carbon steel, copper, silicon, magnesium, and zinc.
Adding an aluminum alloy can improve cast aluminum’s strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance properties.
Injecting The Molten Aluminum Alloy Using a Die Cast Machine
During the high-pressure die-casting process, the die halves are kept securely together by a hydraulic press to stop the leakage of the molten aluminum.
A hydraulic or mechanical system regulates the injection process, which involves forcing molten aluminum into the mold cavity at a predetermined rate of speed.
Cooling and Ejection of Aluminum Parts
This process allows the cast aluminum to solidify and take on its final shape. After the molten aluminum has been injected into the die, a cooling system is used to cool the die cast.
The cooling system typically involves circulating water or oil through channels in the die to remove heat from the molten aluminum.
Cooling depends on the size and complex shapes of the cast metal. Typically, it takes a few seconds to a few minutes. During this time, the die-cast remains in the die, and cooling is controlled for a uniform cooling so that any residual stresses are minimized.
Surface Finishing for Die Cast Aluminum

Sometimes, cast aluminum often requires some form of surface finishing. Shot blasting involves firing small metallic or ceramic particles at the surface of the aluminum products at high velocity. This process helps to remove any surface imperfections and create a uniform surface texture.
Anodizing involves immersing the parts in an electrolytic solution and passing an electric current through them. This causes a controlled oxidation of the surface of the parts, resulting in a hard and durable surface layer with excellent corrosion resistance and better casting properties.
Die Casting Machine Used for Aluminum Casting
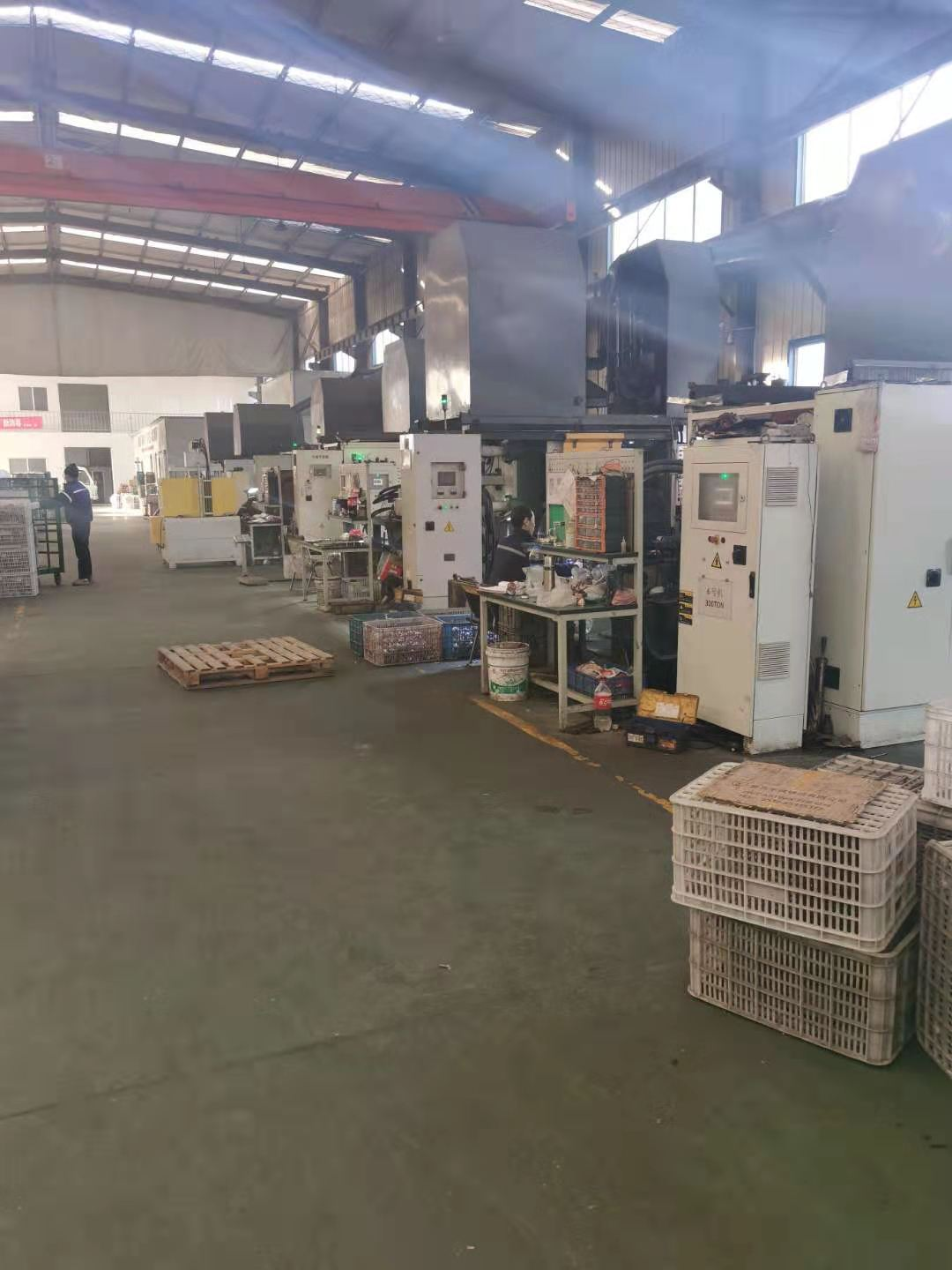

These are specialized machines that inject molten metal. Cold and hot-chamber machines are different, so it is important to understand which is best suited for your project.
Cold Chamber Machine
Instead of melting the metal in the casting machine, as is done in hot chamber machines, metal in cold chamber machines is melted in a separate melting pot.
In cold chamber, molten aluminum is injected into a shot sleeve or injection cylinder. It is hydraulically or mechanically manipulated to force the molten metal into the die mold. This machine is commonly used to produce larger parts or parts that require more precise control.
Hot Chamber Machine for Other Metals
Hot chamber machines are a type of die-casting machine that is used to produce high-volume, small-to-medium-sized parts. Hot chamber machines are designed to melt the metal directly in the machine using a furnace integrated into the die halves.
One of the main advantages of hot chamber machines is their speed and efficiency. The integrated furnace allows for quick and continuous production, particularly when producing high-volume parts. Additionally, the hot chamber process can be automated, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
Aluminum Die Casting Alloy Characteristics
High Strength
Silicon and copper, which are both used as alloying components, contribute to the rise in the alloy’s strength, while the inclusion of magnesium increases the alloy’s resistance to heat and corrosion.
This has the potential to assist increase the part’s strength as well as its other qualities. It is possible for the material’s strength and durability to be improved even more with the use of a later heat treatment.
Lightweight
Aluminum is a low-density metal, with a density of approximately one-third that of steel. This metal is light in nature, but the die casting process makes it more lighter.
The pressurized injection process allows for thin walls and complex shapes to be produced, further reduce the final part’s weight.
Corrosion Resistant
Aluminum is highly resistant to corrosion, forming a thin layer of aluminum oxide on its surface when exposed to air. This layer acts as a protective barrier, preventing further corrosion from occurring.
Similarly, adding other elements can also improve its corrosion resistance. Magnesium and copper can help improve the material’s strength and durability while providing additional protection against corrosion.
Heat Resistance
The addition of silicon to aluminum alloys can improve their heat resistance properties. Silicon helps to improve the alloy’s strength and hardness, which makes it more resistant to deformation at high temperatures
Another element that can improve the heat resistance of aluminum die-casting alloys is magnesium. Magnesium can help improve the material’s strength and durability while protecting against high temperatures. However, it should be noted that magnesium can also reduce the alloy’s ductility, which can affect its overall performance.
Weldability
Aluminum die-casting alloys generally have good weldability, although the specific properties can vary depending on the composition of the alloy. In general, aluminum alloys have a low melting point and excellent thermal conductivity, which makes them relatively easy to weld.
To prevent porosity, it is important to properly prepare the surfaces to be welded and use appropriate welding techniques, such as using a filler material to help fill any voids.
Advantages of Die Casting for Cast Aluminum
High Dimensional Stability

The high-pressure injection allows the molten metal to be distributed evenly throughout the die cavity, ensuring that the finished part has a uniform density and dimensional accuracy.
In addition, the high pressure and rapid cooling of the molten metal as it solidifies helps to minimize shrinkage and distortion, further improving the dimensional stability of the finished part.
The high-pressure injection allows the molten metal to be distributed evenly throughout the die cavity, ensuring that the finished part has a uniform density and dimensional accuracy.
The high pressure and rapid cooling of the molten metal as it solidifies helps to minimize shrinkage and distortion, further improving the dimensional stability of the finished part.
Mass Production Efficiency
A high-pressure injection system drives molten aluminum into a die cavity that has been accurately machined. Once the mold is filled, the aluminum solidifies quickly, allowing for rapid production rates.
Die molds are often constructed from steel or other high-strength materials, and they are built to resist the high temperatures and pressures that are present throughout the casting process. Because of this, they are able to create a high quantity of parts without sacrificing quality or experiencing wear and tear.
Better Mechanical Properties
Fine-grained microstructure with outstanding mechanical characteristics is produced by the fast solidification of molten aluminum in the die cavity. Components with this microstructure are very tough, rigid, and wear-resistant.
Surface Finish

One of the primary reasons for this is that the high-pressure injection system used in the process ensures that the molten metal fills the mold, creating a part with minimal or no porosity, shrinkage, or other defects in the aluminum casting.
The dies are typically made of high-strength materials, such as steel, which allows them to maintain their shape and precision for an extended period. This ensures that the surface of the die is smooth and free from defects, which translates into parts with a good surface finish.
Other Casting Processes for Aluminum Alloys
Sand Casting

The production of aluminum castings also frequently makes use of the process known as sand casting. Sand casting is still a viable option in some circumstances, despite the fact that die casting is the method of choice for mass production because to the efficiency and uniformity it offers.
Additionally, sand casting doesn’t require any specialized equipment or tooling of any kind, in contrast to die casting, which does. This makes it a more cost-effective choice for low-volume manufacturing or for making components with complicated geometries, both of which would be difficult or impossible to create using die casting.
Permanent Mold Casting

One of the primary advantages of permanent mold casting is its ability to produce parts with a higher degree of accuracy and consistency than sand casting. The permanent molds are typically made of metal and can be used repeatedly, ensuring that the metal parts produced are consistent in size, shape, and surface finish.
The molds can be designed to accommodate intricate shapes and features, which makes permanent mold casting a good option for producing parts with high levels of detail.
Investment Casting

Investment casting has been practiced for millennia, yet it has been perfected and updated continuously up to this day. It can make parts with high-quality finishes without resorting to costly and time-consuming additional machining or finishing processes.
In die casting processes and permanent mold casting process, castings are made in high volume production runs. In contrast, investment casting is best for smaller runs because its process is meticulous and involves pouring molten metal carefully.


