Testing cast steel parts is essential for ensuring the integrity of the parts and the casting quality. As such, it is essential to understand the importance of testing metal castings before they are used in any product or project.
By testing cast steel parts, manufacturers can be sure that their parts are of the highest quality and will perform as expected. This helps reduce the risk of failure and improve the final product’s overall performance.
It is also important to remember that cast steel testing is not just a one-time event. Sample castings should be tested regularly to ensure they remain in good condition and continue working on their intended application.
Destructive Testing Methods or Mechanical Testing
Destructive testing is a type of testing that is used to evaluate the mechanical properties of metal castings. This testing involves subjecting the parts to extreme conditions and loads to determine their performance limits. The results of the tests can then be used to determine if the parts are suitable for their intended use.
Tensile Testing
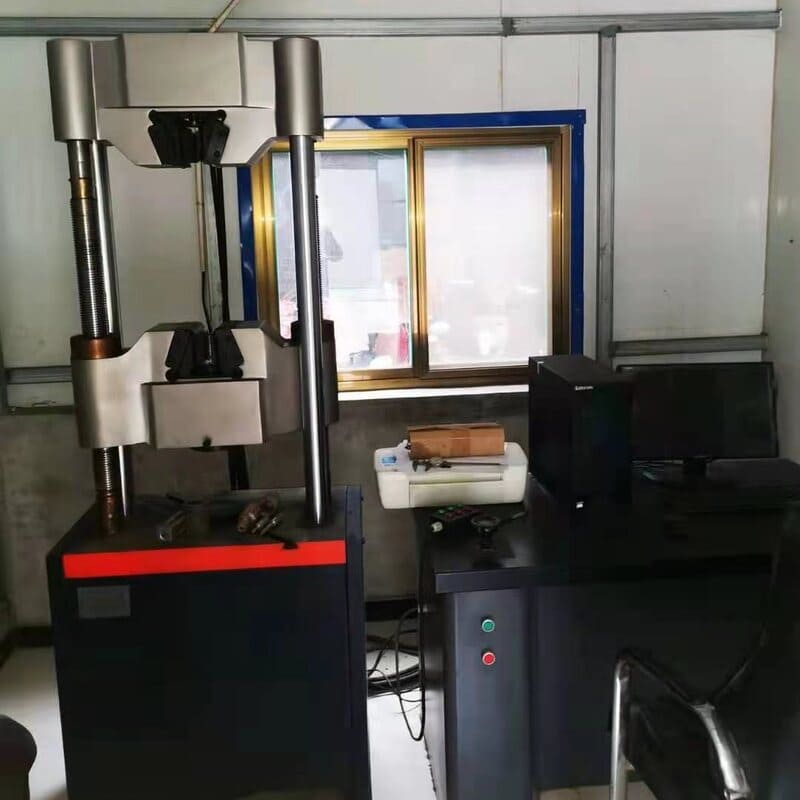

Tensile testing of cast steel parts is a necessary procedure to determine the mechanical properties of cast steel parts. The process involves subjecting the part to a tensile force to measure the force required to break or deform it. This testing ensures that cast steel parts meet the necessary safety and inspection standards.
When performing a tensile test, the part is usually mounted on a testing machine, which applies a force at one end while the other end is held stationary. The force is then increased until the part fails or deforms, at which point the force required to break it is recorded.
The ultimate tensile strength information is then used to determine the strength and ductility. In addition to providing information about the tensile properties of the part, tensile testing can also be used to detect any potential weak spots or flaws in the material.
Impact Testing
Impact testing of cast steel parts is a critical step in the quality assurance of the manufacturing process. It ensures the components are strong enough to withstand the forces they may encounter in normal use.
It is a type of mechanical testing that involves subjecting a sample to a sudden, forceful impact. The test of cast steel parts is done by striking the part with a hammer or other weighted object at a predetermined velocity. The impact force is measured by measuring the displacement of the object or a force gauge.
The impact test is performed to determine the ability of the part to absorb the energy of impact without breaking or failing. It is also used to evaluate the ability of the casting alloys to resist cracking under dynamic loading.
Load Testing
Load testing of cast steel parts using hydraulic methods is a common way to evaluate the strength of a steel part. This testing type involves applying hydraulic pressure to a steel part. The pressure-containing parts are monitored and recorded to determine the strength of the quality casting. The part is then tested using different pressures and loads until the desired results are achieved.
Hydraulically tested metal castings are used in high-stress environments, such as automotive, aerospace, and military applications.
Brinell Hardness Test
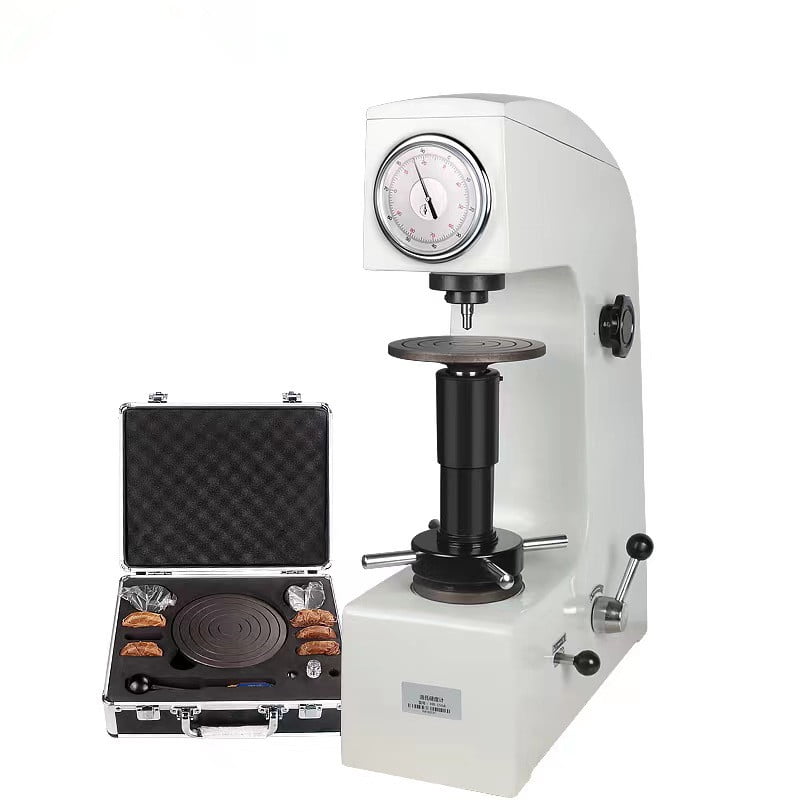

The Brinell hardness test is a widely used method for measuring the hardness and wear resistance of cast steel parts. The test is performed by applying a predetermined force to a steel part using a hardened steel ball.
The depth of the indentation created by the hardness tester is then measured and compared to a hardness chart to determine the part’s Brinell hardness number (HB).
It is useful in Casting because it can measure a wide range of hardness values. The test is also useful for determining whether a part undergoes proper heat treatment and can indicate how the material will perform in service.
Corrosion Testing
The most commonly used method of corrosion testing for cast steel parts is the salt spray test. This is a form of accelerated corrosion testing that involves the application of a salt spray solution to the surface of the steel parts. The solution causes the minor alloying elements of the molten metal to react with the salt, and any corrosion can be detected.
Another method to determine corrosion resistance is electrochemical testing. This type of test can also be used to detect the presence of any contaminants that may be present in the chemical composition of the steel.
Non-Destructive Testing Methods for Test Specimens
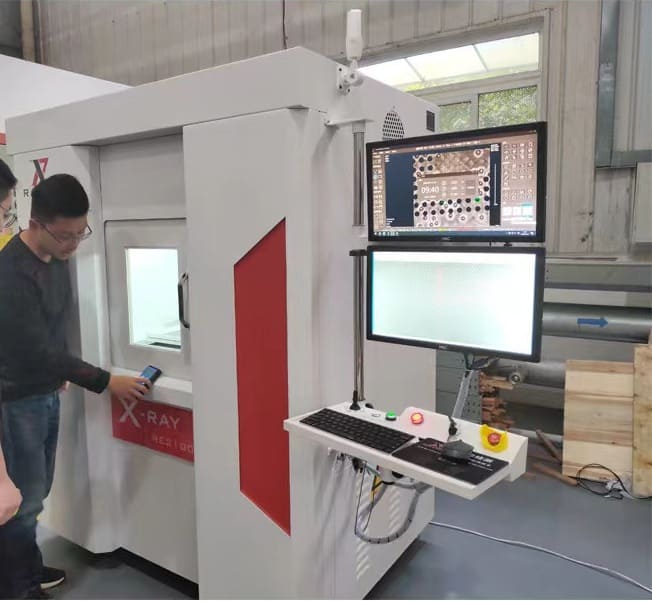

NDT can detect surface cracks, porosity, surface discontinuities, and other defects that could lead to the failure of the steel parts. It is a cost-effective and reliable method of ensuring that the parts are safe and fit for use.
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection of cast steel parts involves the examination of the part’s surface, shape, and dimensional accuracy. During the inspection, the inspector will look for surface defects, warping, and other signs of improper machining. The inspector will also check for signs of corrosion or oxidation and look for evidence of wear or fatigue.
After the inspection, the inspector will document the findings and make any necessary recommendations. Based on the inspection results, the inspector may recommend adjustments to the chemical composition of the parts or suggest that the parts be reworked or replaced.
Liquid Dye Penetrant Inspection
The liquid dye penetrant inspection process is relatively simple. First, a penetrant solution is applied to the part. This solution is designed to penetrate any cracks or defects that may be present in the material. After applying the penetrant, the part is inspected under ultraviolet light. Any cracks or defects that are present will be visible under the light.
The liquid dye penetrant inspection process is non-destructive and does not damage the part. This makes it a preferred inspection method for many industries, as it does not require any alteration to the part. The process is relatively quick, requiring only a few minutes for most parts.
X-Ray Testing
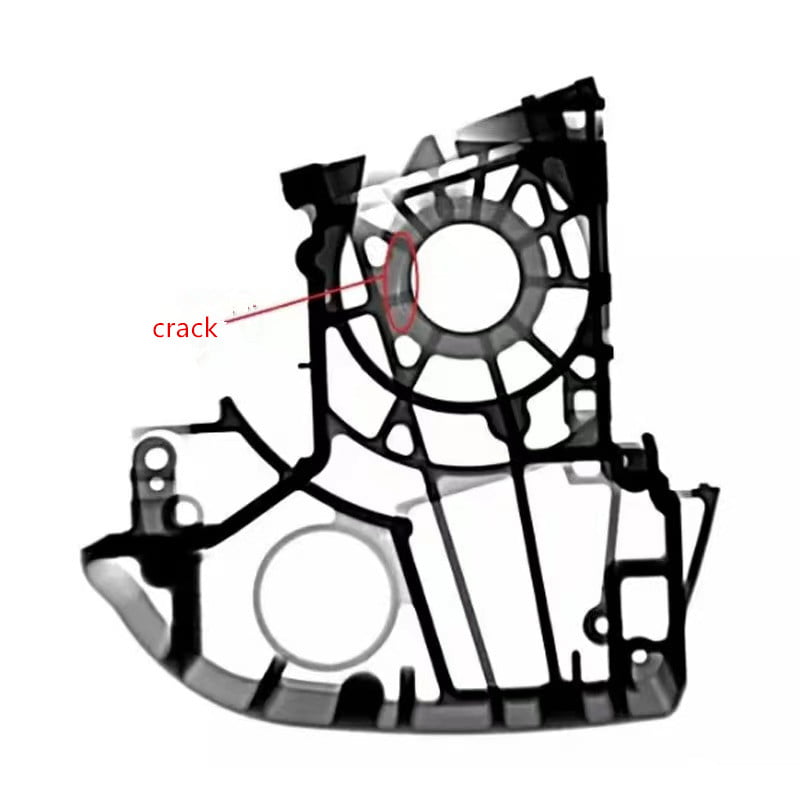
X-ray testing is essential for ensuring cast steel parts’ quality and safety. This form of testing utilizes a special type of radiation to penetrate the surface of the steel and create an image that can be used to detect defects such as slag inclusions, shrinkage cavities, and other imperfections.
When conducting an x-ray inspection of cast steel parts, the inspector must take into account the size, shape, and orientation of the part. The x-ray source must be set up at the correct angle and distance to ensure that the part is properly inspected.
The inspector must also be aware of the limitations of the x-ray source, such as its ability to penetrate thicker parts and detect certain types of defects.
Ultrasonic Testing
Ultrasonic testing is used to detect a variety of flaws, such as cracks, voids, inclusions, and porosity. It is an effective way to inspect thick and complex steel parts that are difficult to reach with other non-destructive testing methods.
It is a non-destructive testing method that uses high-frequency sound waves to detect flaws in steel components. The ultrasonic waves are sent through the steel part and are reflected to the surface when they interact with a defect. This reflected sound wave is then measured and analyzed to determine the size and location of the defect.
Benefits of Metal Testing

This part of the casting process helps identify any manufacturing defects in the cast steel parts. It allows for detecting any impurities or inconsistencies that can lead to the parts being ineffective or even dangerous.
The procedure goes far beyond a visual inspection and can detect any irregularities that cannot be spotted by the naked eye. This means that the parts can be produced with greater accuracy and reliability.
Improved Casting Quality
With the technological advances in metal testing, manufacturers can now achieve improved casting quality in their steel parts. Manufacturers can identify any defects and create a chemical analysis of the steel and make sure that the part is up to the required standards.
This helps them ensure their parts are made from the best materials available.
Reduced Casting Defects
Testing cast steel parts help identify potential defects before they become a problem. Tests such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and destructive testing can detect defects such as porosity, cracks, or internal defects.
By identifying these issues early on, manufacturers can take corrective action before producing the parts. This can help reduce waste and improve the overall productivity of the manufacturing process.
Increased Performance Properties
By testing cast steel parts, manufacturers can identify any potential weak points or defects that could affect the overall performance of the part. This can help to ensure that the part performs to its maximum potential.
For example, testing can help to identify any areas of the part that may be prone to fatigue or corrosion. This information can then be used to improve the design of the part to ensure that it can withstand any potential wear and tear.
Testing can also identify areas where the part may need to be strengthened to improve its performance properties, such as its strength, toughness, and hardness.

