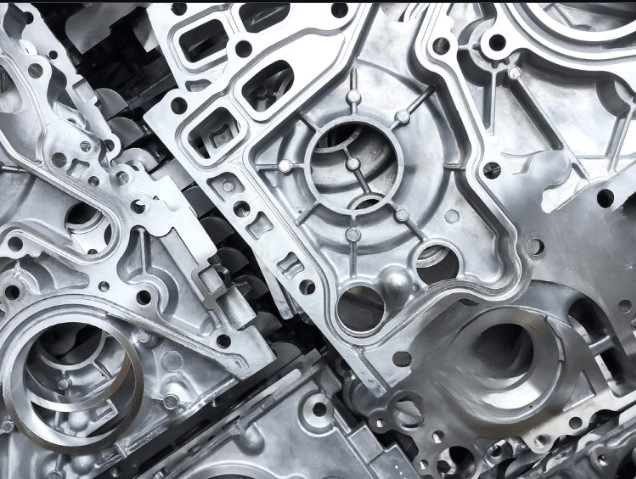
Though both are popular methods for aluminum castings, sand casting vs die cast parts have differences in almost all aspects of the process.
Whether you are a manufacturer looking to optimize your casting process or simply learning more about the two casting methods, this article will provide valuable insights into casting aluminum alloys.
Die Casting Process in Simple Terms

The liquid aluminum is injected to the mold using pressure. It soon hardens and takes on the form of the mold that it was placed in. This process ends up producing a casting that is of a high grade, is exact and detailed, and can be utilized in a variety of different sectors.
Quality Control of Die Cast Aluminum
The quality of the final product can be affected by a variety of factors, such as the quality of the die, the temperature and pressure used during the casting process, and the use of proper lubricants.
These may include visual inspections, measurement of critical dimensions, and various testing methods such as X-ray inspection, magnetic particle inspection, and pressure testing. Effective quality control not only improves the quality of the finished product but also helps to minimize waste and reduce costs associated with product recalls or rework.
Understanding the Sand Casting Process in Simple Terms

It is a cost-effective and efficient way to cast parts with complex shapes and designs. To assure a successful casting, however, it can be time-consuming and labor-intensive and requires skilled operators.
Sand and a binding agent are mixed together to make a mold, which is subsequently compacted around a pattern indicating the final shape of the desired part. Then, it’s removed, leaving a gap in the design.
Quality Control in Sand Casting
To ensure high-quality sand castings, various quality control measures are employed throughout the casting process. This includes monitoring the sand properties, such as grain size and moisture content, to ensure consistent casting results.
The temperature of the molten metal is also closely monitored to ensure it is within the optimal range, while the design of the mold is checked for any defects that could affect the quality of the casting.
Primary Difference between The Two Casting Processes of Cast Aluminum

Materials Used for Molds
This can be done through various methods, such as CNC machining, 3D printing, or manual casting. Die casting requires a metal mold created using a computer-aided design (CAD) program. It requires precise preparation of the mold, which can take several weeks to create.
It can withstand high temperatures and pressures. It can be reused and immediately ready for another die-casting process.
On the other hand, sand casting is a more straightforward process. It requires less time for preparation than other casting methods. It only uses a mixture of packed sand and a binding agent to create the mold.
Entire Process
Die-casting method is commonly used for high-volume production of small to medium-sized parts. The process is also highly automated.
Sand casting is done manually by workers. A sprue is a conduit that permits molten aluminum to flow into the mold, and it is through this channel that the molten aluminum is poured into the mold.
Overall Cost
Die casting is typically more expensive due to the costs associated with tooling and equipment. Sand-casting molds are low-cost and easier to produce. However, the resulting metals may have more variability and require more post-processing work.
Mass Production Efficiency
Die-casting machines can produce a large number of parts quickly and accurately, and the process can be highly automated to further improve efficiency. Additionally, the use of multi-cavity dies can increase production rates even further.
The creation of the sand mold in sand casting is a time-consuming process, and each mold can only be used once before it needs to be replaced.
Die Casting vs Sand Casting Final Product

Dimensional Accuracy
Hot chamber and cold chamber machines in die casting have different capabilities in injecting with high pressure to steel mold in terms of precision and repeatability. High-quality machines are typically equipped with advanced controls and sensors that help to ensure consistent production of accurate parts.
A lesser degree of dimensional precision is achieved as a result of the intrinsic variability of the sand mold, which exists despite the fact that sand casting offers greater design flexibility in terms of the mold itself.
Machining Requirements
Die castings are close to its final form and requires very little machining when the process is complete. It also has an excellent surface finish.
Sand casting produces parts with a rougher surface finish because of the mold material. It may require additional machining operations to achieve the desired final dimensions and surface finish.