Rockwell and Brinell hardness are two of the most common tests used to measure the hardness of iron castings The hardness test is done to determine if the hardness and tensile strength still need to be improved with a machining process, especially in producing rough metal castings. The tests are as important as heat treatment and other manufacturing processes.
The conversion of Rockwell (HR) to Brinell (HB) is relatively simple, but it requires a few calculations.
Rockwell Hardness: Scales and Testing
 Rockwell hardness is a measure of the hardness of a material. In this table, the left side is the scale, while the right-hand column is the best type of metal to use for each scale.
Rockwell hardness is a measure of the hardness of a material. In this table, the left side is the scale, while the right-hand column is the best type of metal to use for each scale.
When using the Rockwell hardness HRC scale, it is important to remember that the scale is only an approximation. Different materials may have different hardness values, and the hardness table shows approximate hardness only. As such, it is important to use the scale as a guide and not as a definitive measure.
Rockwell B Scale
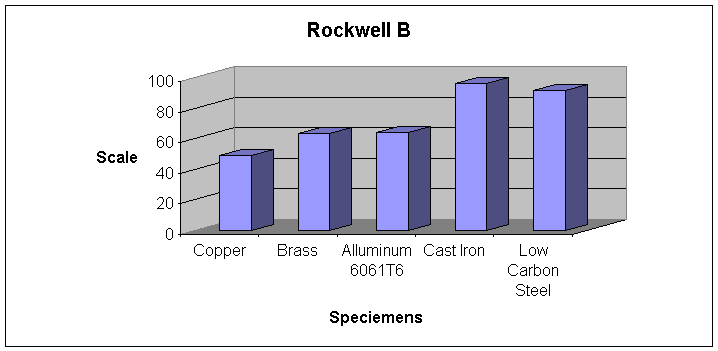 The B HRB scale is most commonly used to measure the hardness of steel, cast iron and alloy metals. It is also used for a variety of other materials including aluminum, brass, bronze and copper. Because it is relatively easy to use and provides consistent and reliable results, it is widely used in industrial settings around the world.
The B HRB scale is most commonly used to measure the hardness of steel, cast iron and alloy metals. It is also used for a variety of other materials including aluminum, brass, bronze and copper. Because it is relatively easy to use and provides consistent and reliable results, it is widely used in industrial settings around the world.
The scale is based on a load of 100 kilograms and is used to measure the depth of indentation in a metal sample. The depth of indentation is measured from the initial zero point to the point where the load is removed using a ball 1/16. The hardness value is then calculated by subtracting the initial zero-point from the final depth of the indentation.
The Rockwell B Scale is a widely used hardness scale developed with a standard ASTM.
Rockwell C Scale
 Rockwell C Scale is a scale used to measure the hardness of a material. It was developed in 1924 by Stanley Rockwell, a metallurgist at the Rockwell International Corporation. The scale uses a small steel ball of fixed diameter that is pressed into the surface of the material being tested. The depth of the ball’s penetration is then measured and converted to a Rockwell C Scale value.
Rockwell C Scale is a scale used to measure the hardness of a material. It was developed in 1924 by Stanley Rockwell, a metallurgist at the Rockwell International Corporation. The scale uses a small steel ball of fixed diameter that is pressed into the surface of the material being tested. The depth of the ball’s penetration is then measured and converted to a Rockwell C Scale value.
The Rockwell C Scale is widely used in industry, particularly in the automotive and aerospace industries. It is also used in the medical industry to measure the hardness of bones and other medical materials.
Testing The HRC and HRB
 The HRC HRB Test measures hardness on an arbitrary scale; the higher the number, the harder the material. The scale consists of two different parts, the Rockwell C Scale and the Rockwell B Scale.
The HRC HRB Test measures hardness on an arbitrary scale; the higher the number, the harder the material. The scale consists of two different parts, the Rockwell C Scale and the Rockwell B Scale.
The Rockwell C Scale is used to measure the hardness of materials that are harder than steel, such as tungsten carbide, while the Rockwell B Scale is used to measure the hardness of materials that are softer than steel, such as aluminum.
The test machine is used to apply the testing force, and the test block is used as a reference surface for the indenter. The test indenter is a hardened steel or carbide ball with a diameter of 2.5 mm, 5 mm, or 10 mm.
The test is conducted by applying a known load to the material and then measuring the depth of the indentation left behind. The depth of the indentation is then compared to a chart to determine the material’s hardness. The Rockwell Hardness scale is divided into three categories, A, B, and C, with A being the softest and C being the hardest.
To conduct the HR Test, a test specimen is placed in a testing machine, which is then loaded with a specific weight. The material is then pressed against a diamond cone or steel ball, which is left in place for a set amount of time.
Brinell Hardness: Measuring and Testing
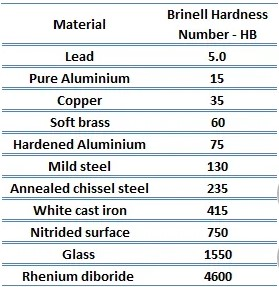 Brinell hardness can be used in measuring hardness of materials. It is a measure of the material’s resistance to abrasion and indentation and is an important factor in determining the strength and durability of metal components.
Brinell hardness can be used in measuring hardness of materials. It is a measure of the material’s resistance to abrasion and indentation and is an important factor in determining the strength and durability of metal components.
It is also used to compare different grades and types of metal and to check the consistency of production batches. It enables engineers to compare different materials and ensure that they meet the desired performance criteria.
Testing Brinell Hardness HB
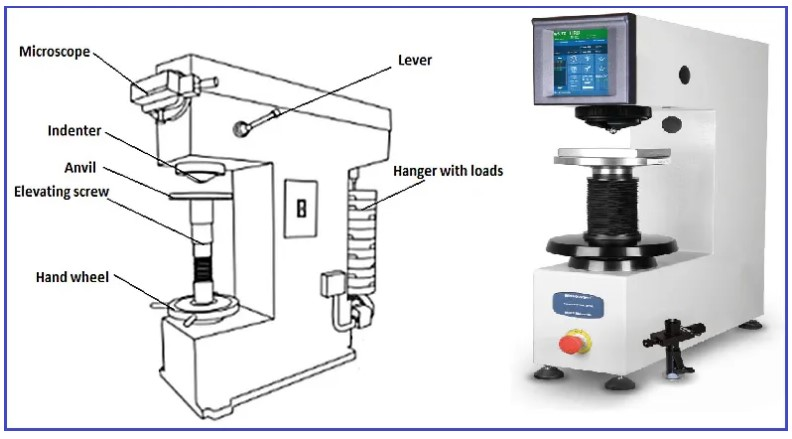 The size of the area of contact between the material and the force applied using the tester will be the Brinell Hardness number. Using the hardness conversion chart, the results can be converted into a numerical value.
The size of the area of contact between the material and the force applied using the tester will be the Brinell Hardness number. Using the hardness conversion chart, the results can be converted into a numerical value.
The test is done by a machine where it presses a carbide sphere into a metal surface. A predetermined amount of force is applied. To determine the hardness rating, measure the diameter of the resulting indentation.
This is usually done by referring to the manufacturer’s specifications or by testing the material with a Brinell Hardness Tester. Once the force is known, the size of the area of contact should then be determined. The force used is multiplied by the area of contact.
Conversion of Rockwell Hardness (HRC) to Brinell Hardness (HB)
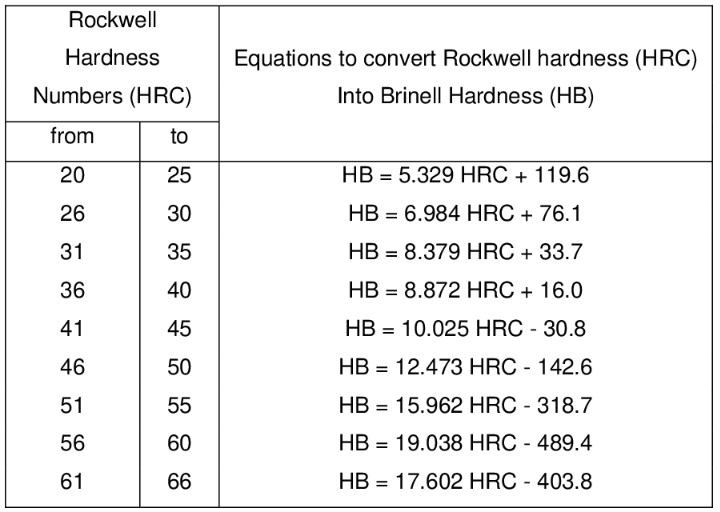 For every one-point increase in HRB, the corresponding result on the Brinell scale will increase by 0.7843.
For every one-point increase in HRB, the corresponding result on the Brinell scale will increase by 0.7843.
Many websites provide online conversion calculators that allow you to convert HR to another scale of measurement. The calculator will take the HR as input and calculate the equivalent value in the desired scale.
Hardness Conversion Chart (Vickers Hardness, Tensile Strength – n/mm, HR, and HB)
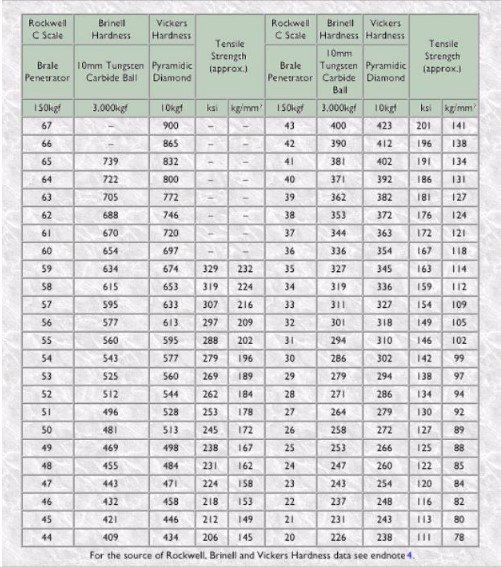 A hardness conversion table is an essential tool for anyone working with metals. These conversion hardness tables provide a quick and easy way to compare the hardness of different metals, including the approximate equivalent tensile strength. It allows engineers and other professionals to quickly evaluate the suitability of a particular metal for a given application.
A hardness conversion table is an essential tool for anyone working with metals. These conversion hardness tables provide a quick and easy way to compare the hardness of different metals, including the approximate equivalent tensile strength. It allows engineers and other professionals to quickly evaluate the suitability of a particular metal for a given application.
The comparison tables are designed to compare hardness values between different scales. For example, you can convert from HRC to HB Rockwell C hardness in its nearest values or convert HRB to HRC Rockwell. You may also easily convert HRC to HB, HV, or refer to Vickers Scales. This allows comparisons to be made between metals that may be measured on different scales.
However, there are no accurate conversion tables. It is important to remember that the results from these conversion charts should be used as a guide only. Different materials can have different properties, even if they have the same hardness rating on a particular scale.
Difference of Rockwell and Brinell Hardness Test
The main difference between the Rockwell and Brinell hardness tests is that they use different conversion factors to convert the amount of force into a hardness value.
This means that different materials may require different methods and factors in conversion. Therefore, the results may not be directly comparable.


