Steel is an incredibly important material for the modern world. Its corrosion resistance, tensile strength, durability, and versatility make it perfect for use in a variety of industries and applications.
The steel industry is one of the most important and influential industries in the world. Steel is an essential material in the construction of buildings and infrastructure, and is also used in the manufacture of vehicles, gas pipelines, and power generators. In this article, you will understand how steel is made, its material properties, and the raw materials used to create steel.
Raw Materials

Steel production is a complex process that involves the use of a variety of raw materials, including iron ore, limestone, coke, and even scrap steel. The different alloying elements used in modern steels and their importance in the fabrication of this versatile material.
Iron Ore
Iron ore is an incredibly important mineral resource that is used in various applications around the world. Pure iron is one of the most abundant metals on the planet and is found in the earth’s crust. It is also the primary source of iron for steel products and cast iron.
It is extracted from the ground using powerful machines and then processed in order to be converted into usable products. The ore is typically separated into different grades based on its final composition and then shipped to steel mills for further processing.
The iron ore is heated to high temperatures using blast furnaces. This process breaks down the iron ore into its component elements, including iron, carbon, and other elements. The iron is then separated from the other elements and is then used in making steel. Once the iron has been separated from the other elements, it is then treated with oxygen and other chemicals to create a molten iron.
Pig Iron
Pig iron is created by combining iron ore with coke and limestone in a blast furnace. The resulting material is a coarse-grained, gray-black material that is extremely hard and brittle. The carbon content of pig iron makes it difficult to work with, but it is a necessary ingredient in the production of steel and other alloys.
It is melted in a furnace, and then various amounts of alloying elements are added to create different types of steel. The molten steel is then processed and formed into the desired shape. Pig iron is also used to make cast iron and wrought iron, which is used in a variety of applications.
Coke
Coke is a strong and durable product that has been used in the steel industry for centuries to create high-quality steel products. It is created in a process called coking. In this process, coal is heated in an oven without oxygen until it becomes a carbon-rich material known as coke. Burning coke alters the coal’s chemical structure, making it more reactive than raw coal and therefore more suitable for use in steel.
It is a hard, black, porous material made from coal that is produced in a special oven and then cooled and crushed into small pieces. The use of coke in steel manufacturing is not just limited to the blast furnace. It is also used in the production of aluminum, copper, and other metals.
Coke is used to create steel for several reasons. It acts as a fuel, providing energy for the steel-making process. It is also has a carbon content, which is essential for creating the alloy steels. This material reduces impurities and helps to improve the overall quality of the steel, ensuring a consistent and superior product.
Limestone
Limestone is an abundant and relatively inexpensive material with many beneficial properties that make it ideal for use in making molten steel. It has a low melting point and a high thermal conductivity, meaning it is able to help maintain a uniform temperature in the furnace and can also help to keep the furnace clean.
When limestone is heated, it decomposes into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. The calcium oxide reacts with the impurities in the iron ore, causing them to melt and form a slag.
The molten slag floats, which be skimmed off the surface of the molten iron using a slag notch. It allows the pure iron to be poured into molds and used to create steel.
Scrap Steel Alloys

Scrap steel is made primarily from industrial products including automotive parts, construction materials, and appliances. It is collected at scrap yards, and then sorted and processed into various grades of steel. The recycled steel is then melted down and re-formed into new products such as steel plates, beams, and rods.
The recycling process of scrap steel helps reduce the need to create new steel. This helps to conserve energy, reduce the number of materials used, and reduce carbon dioxide emissions. It also helps to reduce the amount of waste that needs to be disposed of in landfills.
Modern Production Methods of Steel
Blast Furnace
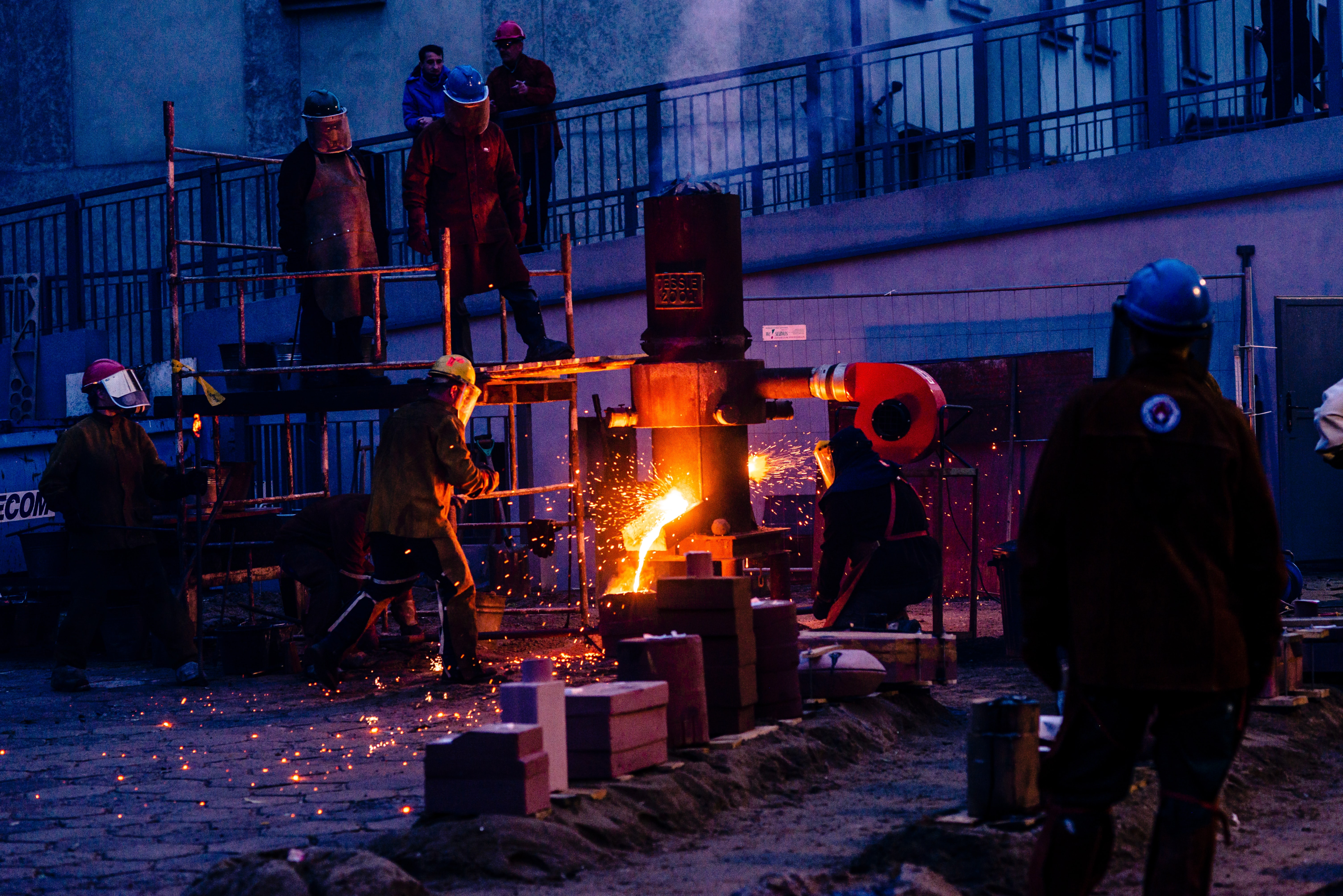
The blast furnace process has been improved and refined over the years, allowing for greater efficiency and larger production capacities. Modern blast furnaces are highly automated and computer-controlled, allowing for greater precision and increased safety.
This method is ideal for mass production as it is capable of producing a large amount of steel in a short amount of time. The process is also highly cost-effective, as the materials used in the blast furnace are relatively inexpensive.
Additionally, the blast furnace process is highly energy-efficient, as the heat generated from the burning coke is used to heat the furnace and smelt the ore.
Electric Arc Furnace

Electric arc furnaces (EAFs) are increasingly being used as a modern production method for steel. By using electric current to heat scrap steel, these furnaces can produce new steel quickly and efficiently. This method has become popular in recent years due to its energy efficiency and low cost.
The arc is generated by the electrical energy that passes through the electrodes, which are connected to the furnace. As the current passes through the electrodes, it creates high temperatures that melt the recycled steel.
Production Process of Steel
Steel is one of the most versatile and widely used materials in the world, with a wide range of applications from construction to automotive and beyond. The production process of steel is a complex and labor-intensive one, involving multiple stages and techniques.
Melting and Refining
The first step in making most steel is melting the raw materials. This is done by using high heat, usually in the form of a furnace. The hot metal will turn into a liquid, which is then poured into a steel ladle.
In the ladle, the steel is further refined by adding other materials such as alloys, pig iron, and scrap metals. These are all melted together and combined to create the desired composition of the steel.
Casting

Casting is one of the most important steps in the production process of steel. Casting involves the process of pouring molten steel into pre-shaped molds, which then cools and hardens into the desired shape.
Once the steel has cooled, it is then inspected to ensure that it meets all of the desired specifications and requirements. In some cases, the steel may need to be machined or cut to the exact specifications that are required. The casting process is then complete, and the steel is ready for use.
It is highly customizable, allowing manufacturers to create products with complex shapes and sizes.
Rolling and Forming
Rolling and forming are two important processes for creating steel products. These processes are used to create a range of shapes, sizes, and thicknesses from steel.
Rolling shapes the steel into the desired form. It is a process of mechanically deforming steel by passing it through rollers. This process reduces the thickness of the steel while increasing its length and width. Cold rolling is done to create a wide range of products, such as sheets, tubes, and rods.
Forming is used to create shapes that cannot be created through rolling. It involves pressing the steel into a form or die. The steel is placed in the form and then heated up to form the finishing steel into the desired shape. This process is used to create components such as gears, cams, and flanges.
Types of Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon steels are resistant to corrosion and can withstand extreme temperatures without losing their structural integrity. It also has a high tensile strength, which makes it suitable for a variety of applications. Additionally, carbon steel is an affordable material, making it a popular choice for a variety of projects.
Carbon steel can be treated in a variety of ways in order to increase its strength and durability. Common treatments include heat treatment, annealing, and quenching. These treatments can also be used to increase the material properties of the metal.
Different types of carbon steels include high-carbon steel and low-carbon steel. Both have different properties appropriate for specific use.
Alloy Steel
Alloy steel is a type of steel that is composed of iron and other elements, such as carbon, manganese, chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, nickel, and silicon. Such alloys are added to the steel to improve specific properties such as strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance.
Alloy steel is classified into two main types: low-alloy steel and high-alloy steel. Low-alloy steel contains less than 5% alloying elements, while high-alloy steel contains more than 5%.
Tool Steel
Tool steels are made up of a variety of metals and alloys, including iron, carbon, manganese, silicon, chromium, tungsten, and molybdenum. Depending on the application, tool steel can be either heat treated for better mechanical properties.
It is often used in applications where extreme temperatures are encountered, such as in machining, forging, and die-casting. This makes it a popular choice for applications that needs to be heat-resistant, such as aerospace and automotive components.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an alloy that is composed of at least 10.5% chromium, as well as iron, nickel, carbon, and other elements. The chromium content in stainless steel gives it its corrosion-resistant properties, making it a popular choice for products that will come into contact with corrosive substances.
In addition to being corrosion-resistant, stainless steel is also known for its strength, making it an ideal choice for many construction applications, such as reinforcing steel beams and columns.


